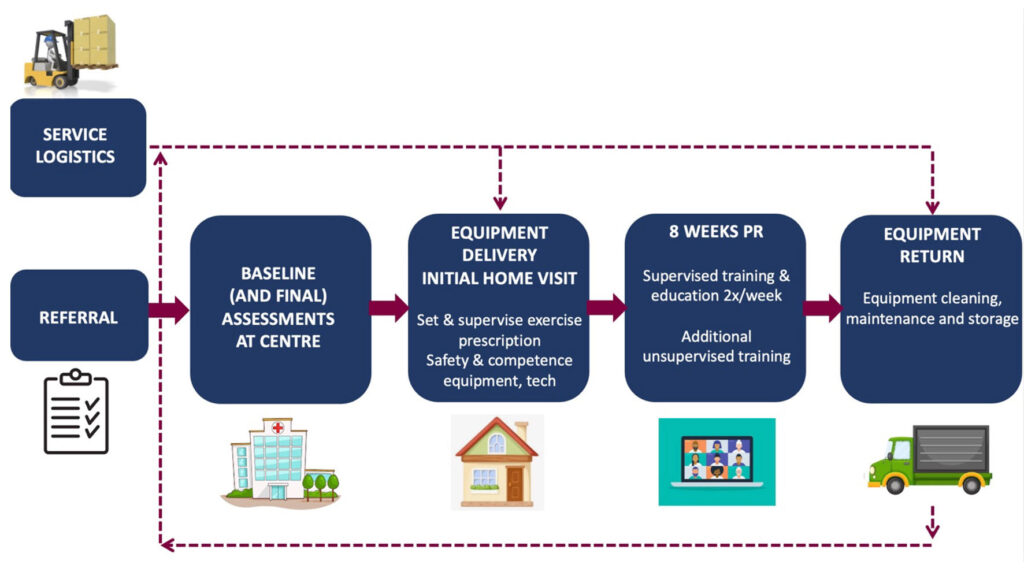
Interaction between service logistics and program delivery for telerehabilitation model using advanced technology and exercise equipment.
Home Visit
Following thorough patient assessment, but prior to commencing their first virtual group training session, for telerehabilitation models making use of advanced technology and exercise equipment a home-visit with the physiotherapist is recommended. The goals of the home-visit are to:
- Ensure safety and confidence to use equipment and technology
- Prescribe and supervise first exercise training session
- Complete home exercise diary
- Provide and explain Borg scales
- Check inhaler technique (as relevant) & address any education/health goals
- Review emergency procedures
Pre-visit
- Arrange and confirm delivery of relevant equipment to be in place prior to home-visit. In keeping with local policy ensure courier is COVID compliant as necessary.
- Confirm patient contact details
- Complete home-visit preparation checklist
- Collect relevant equipment to take on visit eg. Oxygen saturation monitor, tablet computer etc
- Complete home-visit safety checklist and other relevant institutional screening procedures.
- Review relevant assessment and history details
To undertake a home-visit the visiting health professional must have both a mobile telephone and suitable transportation. Prior to the visit the health professional should confirm if the patient experiences any language or cognitive issues, and ascertain if there will be pets, animals or other people in attendance during the visit that may impact the health professional. Staff undertaking home-visits should review all relevant local procedures, and undertake relevant training, with respect to visiting health worker safety. Additional information on working safely during visiting health services can be found here.
At the visit
- Review/set-up equipment (exercise and technology) – check for any property, environment or manual handling hazards or risks
- Review written instructions for equipment operation with patient
- Familiarise patient with exercise equipment operation and give opportunity to practice operation of equipment
- Familiarise patient with technology equipment operation and video-conferencing access. Demonstrate, and provide opportunity for patient to practice operating technology equipment and accessing video-conferencing platform during a practice call
- Discuss/review patients’ rehabilitation goals (if not already established)
- Review and practice ratings of breathlessness and exertion with Borg scales
- Undertake exercise training session (see also Exercise Training Protocols)
- Review home exercise diary and any rehabilitation or education resources provided to patient
- Confirm dates and times of virtual group telerehabilitation sessions
- Complete home-visit documentation
“The physio came to my home and she actually went through everything with me. So that was fabulous. It was great education and you knew exactly what to expect and how to do it and the setup of everything so that actually made a huge difference. I think if you hadn’t had that, you know, it would have been a bit of a mess, that first session, would have been a real mess"
- Quote from interview with patient undertaking telerehabilitation
Following the visit
- Complete relevant documentation/medical record entry (see example documentation template)
- Handover (as relevant) to telerehabilitation clinician
- Provide patient contact details for telerehabilitation class safety list
Home-visit staff security and safety
The security and safety of the staff member undertaking the home-visit must be strictly monitored. All local institutional policies should be adhered to. Additional considerations for ensuring security and safety of home-visit staff include:
- Attend the visit with a colleague
- Check in on arrival via SMS with a colleague ensuring they are aware of the patients’ address and phone number, time of arrival and anticipated completion time
- Check in on departure via SMS at the completion of the visit once they have left the premises
- Provide the health professional with a duress alarm (eg Work Safe Guardian)
Virtual group telerehabilitation training sessions
Depending on staffing capabilities and network connectivity, a maximum group size of 4-6 participants is suggested. Typically training sessions delivered via video-conferencing would run for around one hour (60mins) and may include delivery of specific education content alongside exercise training, or in a separate session.
Pre-session preparation:
- Ensure ready access to patient notes
- Ready access to participant contact list for in the event of emergency or technology issues
- Web-based, mobile application or manual options for time-keeping (multiple and simultaneous)
- Video conferencing account/log-in details for host
- Ensure telephone available for contacting patient/emergency contact/troubleshooting

Health professional preparing for delivery of virtual group rehabilitation
Example of multi-timer for monitoring patient training duration.
The session
Telerehabilitation sessions will be conducted by an appropriately trained health professional such as a Physiotherapist or Exercise Physiologist. The availability of a second or stand-by clinician in case of technical difficulties or emergency may be ideal/required based on local preference/policy.
- Introduce self and/or any new participants to each other
- Check audio setting for yourself and all participants
- Review each participant in terms of general well-being and health status, specifically checking for symptom status, development of new symptoms, progress etc. *If there are no new symptoms and patients are assessed as stable, they can proceed to complete the supervised training session. If participants’ feel they have a moderate or severe flare-up of their respiratory condition, they should be advised not to exercise and to contact their GP/call for emergency services as necessary.
- Ensure the patient is clearly visible and that and all equipment is visible, turned on and functioning correctly eg. Oxygen saturation monitor is in view and clearly readble; able to see participants’ face and Oxygen saturation monitor in same frame; able to see and hear everyone.
- Commence participants on individualised training schedules (see example exercise training protocol)
- Monitor as appropriate (SpO2, HR, symptoms, Borg, Fatigue, appearance)
- Document training intensity, duration, time, responses, rest periods, progressions (as relevant)
- Flag relevant progressions/goals for next session
- Provide relevant content education in response to specific health goals or group requests (as applicable; may not be relevant where participants are attending separate support group/education session)
- Confirm any planned non-attendance for next session
Managing the deteriorating patient
Escalation of a medically deteriorating patient may be indicated if a patient reports becoming unwell with any of the following symptoms:
- Increased shortness of breath
- Increased coughing +/- sputum
- Changes in sputum colour
- Febrile/Chills
- Increased difficulty performing daily tasks due to any of the above symptoms
- Coryzal symptoms
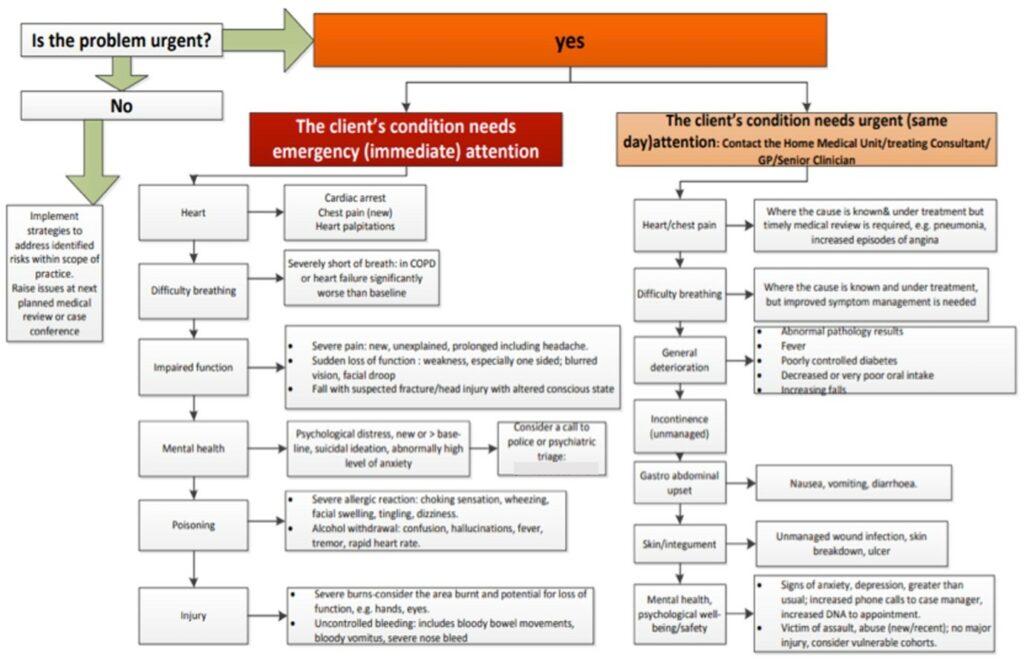
Example of an escalation of care flow chart
Management procedures would be in keeping with clinically appropriate decision-making and local policies, and may include advice to:
- Cease or not exercise
- To contact their local GP/medical provider
- To call for emergency services
"They encourage you to go and see your GP if you’re not feeling too well."
- Quote from interview with telerehabilitation participant
Situations that require calling for emergency assistance immediately include:
- Persistent Chest Pain
- Cardiac Arrest
- Heart Palpitations
- Numbness or slurred speech
- Fall where patient becomes injured and/or cannot get up
- Low oxygen saturation that does not improve with rest
- Severe breathlessness that does not improve with rest
- Severe Pain
- Severe allergic reaction or alcohol withdrawal
- Suicidal ideation, hallucinations or altered conscious status
- Uncontrolled bleeding or severe burns
All clinicians involved in the delivery of telerehabilitation should be familiar with local emergency procedures and the contact for emergency services in their area.
Conclusion of Telerehabiliation
Re-assessment
At the conclusion of the rehabilitation program all participants should be re-assessed in line with usual care incorporating both patient reported outcomes, reassessment of exercise capacity and review of patient set rehabilitation goals.
Collection of equipment
- Arrange and confirm for collection of relevant equipment
- Maintenance and cleaning of all returned equipment in line with local policies



